Review
PV systems can be roof-mounted or ground-mounted. Most systems are grid-tied, while some are off-grid or a hybrid of the two.
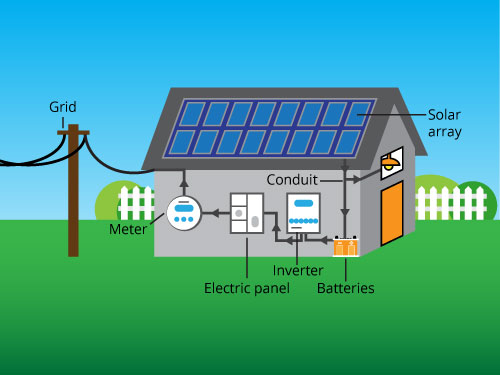
PV systems generally consist of:
- Arrays
- Inverters
- Conduit
- Combiner boxes
- Batteries
- Meters
- Disconnect switches
Potential risks of PV systems include:
- Access limitations
- Structural failure
- Trip or slip hazards
- Enhanced flame spread
- Shock hazards
- Toxins and carcinogens
- Surges and arcing
- Battery hazards
Always assume components are energized, even if the sun is not shining or if PV panels are damaged. After the system is shut off, inverters still pose a shock hazard until they have completely discharged their stored energy.